CT Angiography In Nagpur
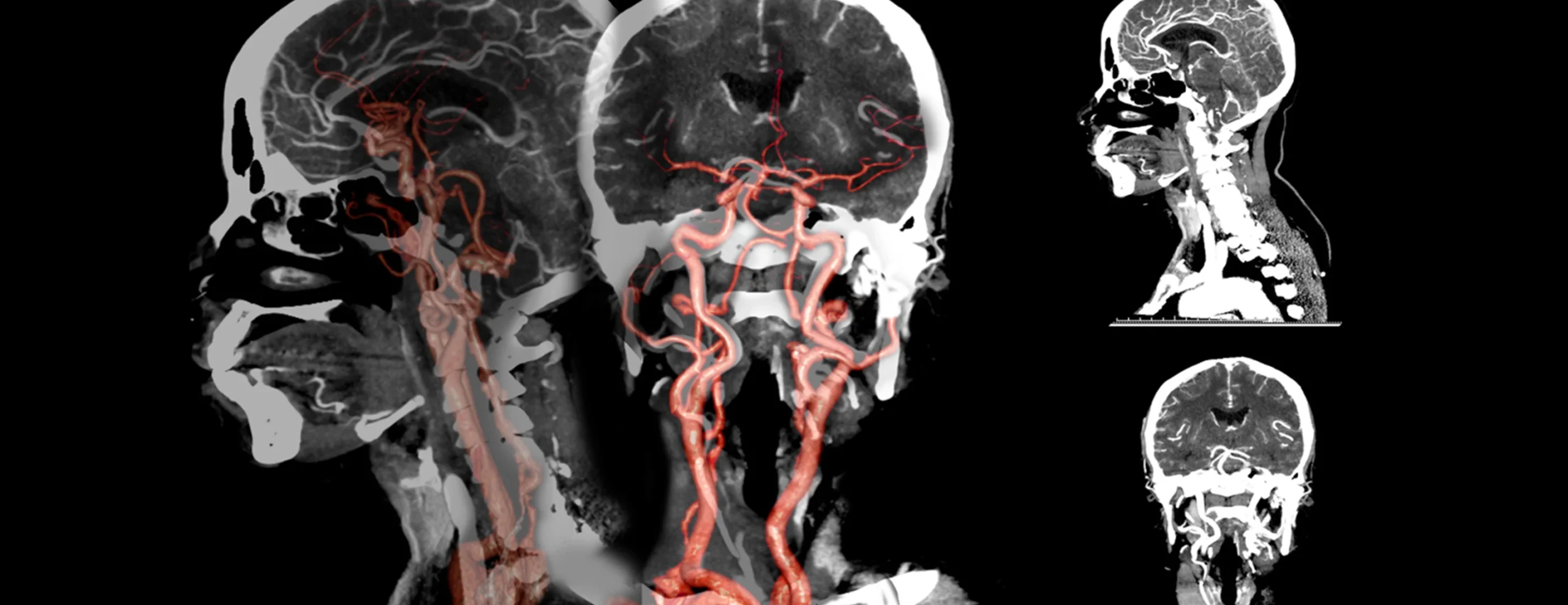
CT Angiography (CTA) is a specialized imaging test that uses a CT scanner and a contrast dye (injected into your bloodstream) to capture detailed images of blood vessels and arteries. This allows doctors to see the condition of vessels in the brain, neck, chest, abdomen, pelvis, and limbs.
CT Perfusion Studies measure blood flow, blood volume, and the time it takes blood to pass through tissues. It is especially useful for evaluating brain perfusion in stroke patients, tumors, or areas with suspected ischemia (restricted blood supply).
Types of CT Angiography and Perfusion Studies
Head CT Angiography and Perfusion: Evaluates brain vessels for aneurysms, strokes, or tumors.
Neck CT Angiography and Perfusion: Checks carotid arteries and blood flow to the brain.
Body CT Angiography: Includes chest, abdomen, and pelvis to assess aortic aneurysms, pulmonary embolism, or visceral organ blood supply.
Extremities CT Angiography: Examines blood vessels in the arms and legs, often used in cases of peripheral artery disease or trauma.
What Are Some Common Uses of the Procedure?
Detecting aneurysms or vascular malformations
Evaluating stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA)
Checking for arterial blockages or narrowing
Assessing tumors and their blood supply
Planning for surgeries or stent placements
Diagnosing blood clots or pulmonary embolism
Evaluating trauma-related vessel injuries
How Do I Prepare for My CT Angiography and Perfusion Studies?
Inform your doctor if you have kidney disease, diabetes, or allergies to contrast dye.
You may be asked to avoid eating or drinking for 4–6 hours before the test.
Remove all metal objects such as jewelry or hairpins.
Wear comfortable, loose-fitting clothing, or you may be asked to change into a gown.
Follow any specific instructions provided by your doctor or imaging center.
What Will Happen During My CT Angiography and Perfusion Studies?
You will lie comfortably on the CT table, which slides into the scanner.
A contrast dye will be injected into a vein, usually in your arm, to highlight the blood vessels.
The CT scanner will take multiple images as it rotates around the area of interest.
For perfusion studies, additional software analyzes blood flow through the tissues.
The procedure usually takes 30–60 minutes, depending on the region being studied.
Afterward, you can generally return to normal activities unless advised otherwise.
What Are the Reasons for a CT Angiography and Perfusion Study?
Your doctor may recommend this test if you have:
Unexplained headaches, dizziness, or fainting
Symptoms of a stroke or mini-stroke (TIA)
Suspected aneurysm, arterial disease, or blockage
Chest pain with suspected aortic or pulmonary problems
Peripheral artery disease symptoms, like leg pain while walking
Cancer, to assess the blood supply to tumors
Trauma with possible vascular injury
Why Is Skeletal and CT Angiography and Perfusion Study Used?
While CTA focuses on blood vessels, skeletal CT angiography provides combined views of bones and vessels, especially useful in:
Pre-surgical planning for complex bone and vascular injuries
Evaluating tumors near bone structures
Diagnosing fractures with associated vascular damage
Assessing blood flow around orthopedic implants or prostheses. book an appointment at Nobel Imaging and Diagnostic for a medical test
In some cases, a contrast dye may be injected to enhance the visibility of certain tissues or blood vessels. If needed, our staff will discuss this with you beforehand. Contact Us
