MRI Breast
Types of MRI – Including Whole Body MRI
we offer multiple types of MRI scans tailored to the patient’s needs:
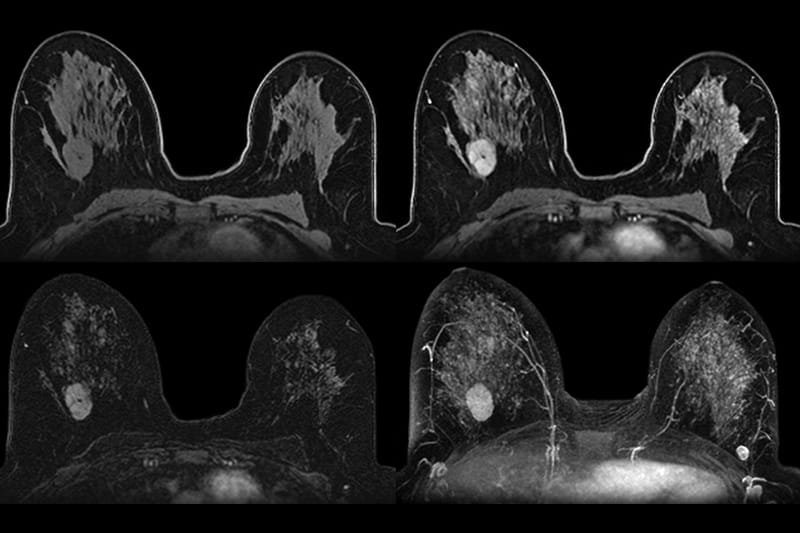
MRI Breast – Focused imaging of breast tissue, often used in cancer detection or implant evaluation.
MRI Breast with Contrast (Gadolinium Injection) – Provides enhanced detail and helps distinguish between benign and malignant lesions.
Whole Body MRI – A comprehensive scan of the entire body to detect tumors, inflammation, infections, or metastasis. Ideal for cancer staging or screening high-risk individuals.
What are Some Common Uses of the Procedure?
MRI Breast is commonly used for:
Screening high-risk patients (especially those with a family history or genetic mutations like BRCA1 or BRCA2)
Evaluating abnormal mammogram or ultrasound results
Detecting the extent of breast cancer
Monitoring response to chemotherapy
Examining breast implants for rupture or leakage
Differentiating scar tissue from recurrent cancer
Planning for surgery or radiation treatment
How Do I Prepare for My MRI Breast?
Preparation for a Breast MRI is usually simple:
Wear comfortable, metal-free clothing or change into a provided gown.
Remove all jewelry, hairpins, or metal accessories.
Inform the technician if you have any metal implants, pacemakers, or allergies.
If contrast dye is used, disclose any kidney issues or past allergic reactions.
If you are menstruating, the scan may be scheduled between days 7–14 of your cycle for clearer images.
What Will Happen During My MRI Breast?
During the procedure:
You will lie face-down on a padded MRI table with your breasts positioned into cushioned openings.
The table slides into the MRI machine, and you must remain still.
The scan typically takes 30–45 minutes.
If contrast is needed, it will be injected through a vein in your arm before or during the scan.
You may hear loud thumping or tapping sounds—earplugs or headphones will be provided.
The procedure is painless and you can resume normal activities immediately afterward.
What Are the Reasons for an MRI Breast?
Doctors may recommend a Breast MRI for the following reasons:
To detect breast cancer in high-risk women
To evaluate the size and spread of cancer before surgery
To monitor changes in known benign breast conditions
To screen women with dense breast tissue
To check for implant rupture or leakage
To follow up on suspicious findings from other imaging tests
Why is Angiography Used in Breast MRI?
Angiography in breast MRI involves using contrast agents to evaluate blood flow within breast tissue. This helps:
Distinguish between benign and malignant lesions (cancerous tumors often have more blood supply)
Detect early-stage cancers not visible on standard imaging
Assess tumor vascularity, which can influence treatment planning
Contrast-enhanced MRI is often a vital component of breast angiography, offering enhanced visualization for more accurate diagnosis and treatment.
