NT/NB Scan In Nagpur
Expecting a baby is a journey full of emotions, hope, and responsibility. One of the most critical aspects of pregnancy care involves early screening tests, especially the NT/NB scan, which is essential for assessing the health of your baby during the first trimester. This scan not only provides valuable insights into your baby’s development but also detects potential chromosomal abnormalities early on.
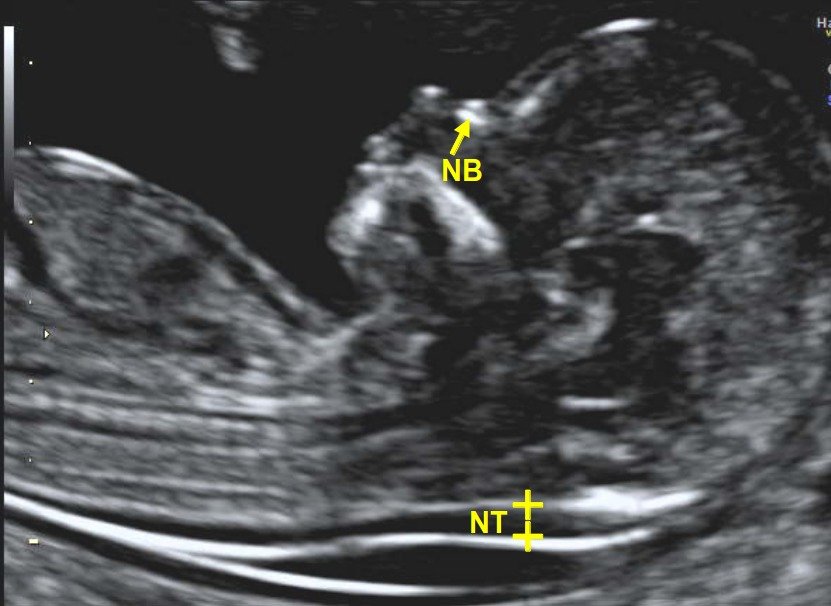
What is an NT/NB Scan?
Nuchal Translucency (NT): This refers to fluid-filled space at back of baby’s neck. An increased NT measurement can indicate a higher risk of chromosomal abnormalities such as Down syndrome (Trisomy 21).
Nasal Bone (NB): The presence or absence of the nasal bone is evaluated. Studies show that in certain genetic disorders, the nasal bone may be underdeveloped or absent during early pregnancy.
When is the NT/NB Scan Done?
11 weeks to 13 weeks + 6 days from gestation
The crown-rump length (CRL) of the fetus must be between 45 mm and 84 mm for accurate results.
Importance in Prenatal Screening
The NT/NB scan forms cornerstone of first-trimester screening. While modern technology has made it easier to assess fetal health, this scan remains one of the earliest and most accessible tools to evaluate genetic and developmental risks.
- Detects common chromosomal abnormalities: Particularly Down syndrome (Trisomy 21), Trisomy 13, and Trisomy 18.
- Part of the “Combined First Trimester Screening”: When paired with a blood test (measuring free β-hCG and PAPP-A), it increases diagnostic accuracy up to 85–90%.
- Early identification of structural issues: Especially cardiac defects and neural tube defects that may require advanced imaging later in the pregnancy.
Guides decision-making: Helps doctors determine whether further testing like NIPT, amniocentesis, or CVS is needed.
How the NT/NB Scan is Performed
- Abdominal ultrasound: Most NT/NB scans are done via abdominal ultrasound. Gel applied to your belly and transducer is moved over it.
- Transvaginal ultrasound: Sometimes used for better imaging, especially in early weeks or if the baby is in an awkward position.
- The sonographer measures: Nuchal translucency thickness in millimeters. , Presence and structure of the nasal bone. ,Crown-rump length (CRL) to determine gestational age.
- A risk factor ratio is calculated (e.g., 1 in 500, 1 in 1000).
- Combined with blood test results, maternal age, and history to generate a risk report.
- The entire experience is painless and usually does not require any recovery time.
Normal vs. Abnormal Results
- Typically less than 3.0 mm when measured between 11–14 weeks.
- Most healthy babies have NT measurements between 1.2 mm and 2.5 mm.
- Down syndrome (Trisomy 21)
- Trisomy 13 or 18
- Turner syndrome
- Congenital heart defects
- Diaphragmatic hernia or other structural issues
Conditions Detected by NT/NB Scan
- Down Syndrome (Trisomy 21): Most commonly detected through increased NT and absent/hypoplastic NB.
- Edwards Syndrome (Trisomy 18): Associated with structural anomalies and increased NT.
- Patau Syndrome (Trisomy 13): May be associated with increased NT and multiple anomalies.
- Turner Syndrome: Seen in female fetuses with cystic hygroma (very large NT).
- Congenital Heart Defects (CHD)
- Omphalocele or abdominal wall defects
- Diaphragmatic hernia
- Limb or skeletal abnormalities
- A severe form of increased NT—may indicate Noonan syndrome or genetic mosaicism.
book an appointment at Nobel Imaging and Diagnostic for a medical testIn some cases, a contrast dye may be injected to enhance the visibility of certain tissues or blood vessels. If needed, our staff will discuss this with you beforehand. Contact Us
