Shear wave / strain elastography for Liver, Breast, Thyroid etc.
Shear wave elastography (SWE) uses sound waves to measure how fast “shear waves” move through tissue, giving a precise, quantitative measure of tissue stiffness. Stiffer tissue often indicates fibrosis, tumors, or other disease processes.
Types of Shear Wave / Strain Elastography
Liver Elastography – Assesses liver stiffness to detect and monitor fibrosis, cirrhosis, or fatty liver disease.
Breast Elastography – Helps distinguish benign from malignant breast lesions.
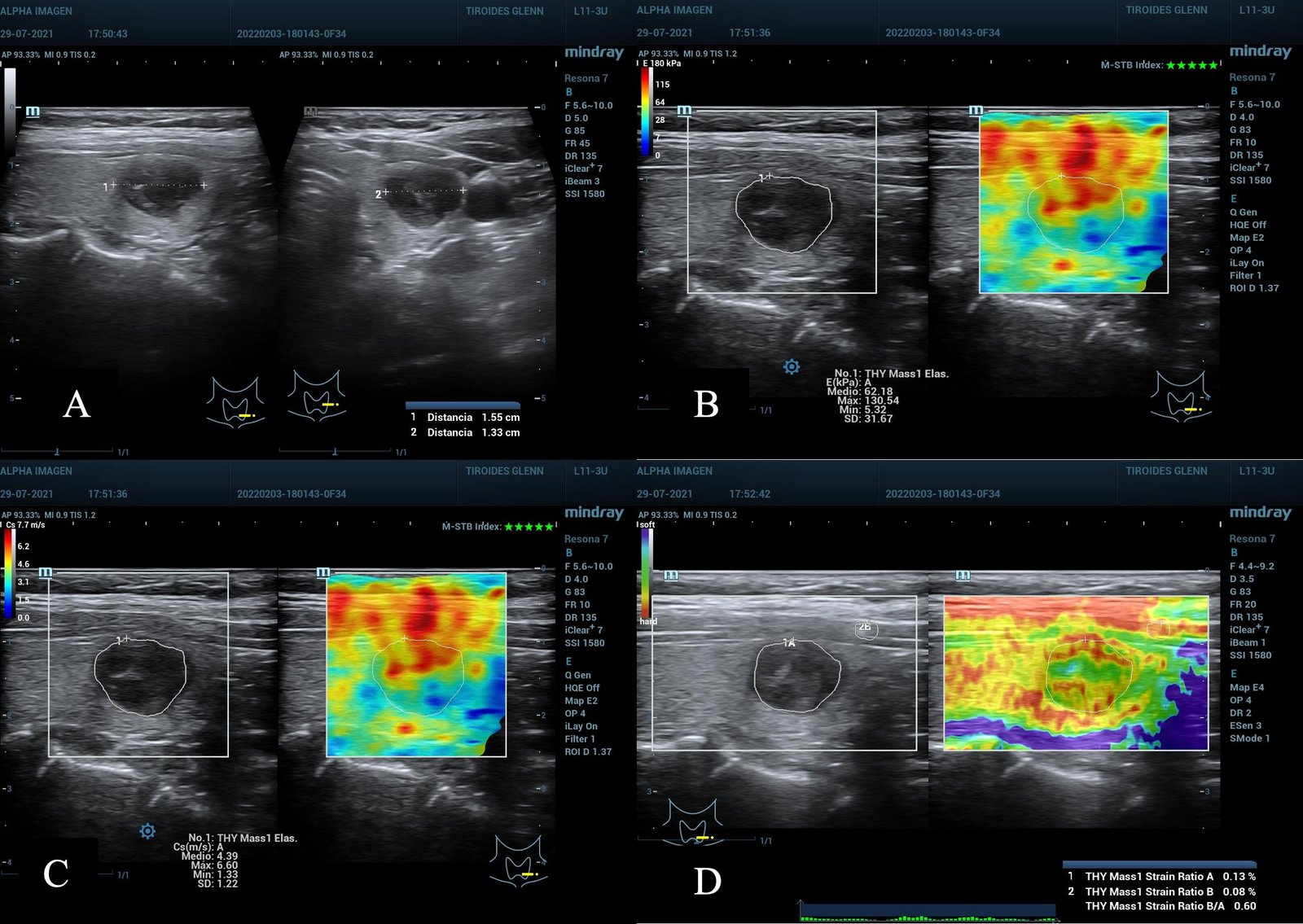
Thyroid Elastography – Evaluates thyroid nodules and helps assess the risk of thyroid cancer.
Prostate and Lymph Node Elastography – Assists in evaluating prostate stiffness and suspicious lymph nodes.
Symptoms That May Lead to Elastography Evaluation
You may be referred for elastography if you have:
Persistent liver disease or abnormal liver blood tests
History of hepatitis B or C, alcohol-related liver disease, or fatty liver
A newly found breast lump on mammography or ultrasound
Thyroid nodules detected on physical exam or ultrasound
Enlarged lymph nodes or suspected prostate abnormalities
Common Uses of Shear Wave / Strain Elastography
Liver: Assess fibrosis stage in chronic liver diseases; monitor liver health without biopsy.
Breast: Improve cancer detection; differentiate benign from malignant lumps.
Thyroid: Characterize thyroid nodules; reduce unnecessary biopsies.
Prostate & Lymph Nodes: Identify abnormal tissue, guide biopsies if needed.
How to Prepare for Shear Wave / Strain Elastography
In most cases, no special preparation is needed. For liver elastography, you may be asked to fast (avoid food and drink) for 2–4 hours before the exam to improve image quality. Wear comfortable clothing, and you may be asked to remove jewelry near the area being examined.
What Happens During the Procedure
You will lie comfortably on an examination table.
A water-based gel is applied to the skin over the area being evaluated.
The ultrasound probe is gently placed on the skin. For strain elastography, light pressure may be applied.
The machine captures stiffness measurements and creates color-coded images.
The entire procedure typically takes 15–30 minutes and is completely painless.
Reasons for Shear Wave / Strain Elastography
Doctors recommend elastography to:
Detect early liver fibrosis or cirrhosis
Evaluate suspicious breast or thyroid nodules
Guide decisions about the need for biopsy or further tests
Monitor treatment response in liver or cancer patients
Provide additional diagnostic information beyond regular ultrasound
